What is power
factor?
The cosine of Angle
between voltage and current is call power factor.
Explanation:-
We have three types of power
1- “VA” Volt Ampere
2- “W” Watt
3- “VAR” Volt
Ampere Reactive
“VA” Apparent power
This power we give
to our equipment.
“W” Active Power
As much power
appliances take.
“VAR” Reactive power
As much power our
equipment wastes.
The power factor is
Ratio between two powers such as “VA” and “W”, and it denoted by cos(θ) or P.F.
The power factor will create only in “AC" current not in “DC"
current, because “DC" current not has frequency.
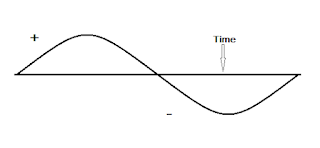
The power factor will create in which current has frequency. You know that in the "AC" current has frequency which is 50 hertz. The "AC" current create a waveform, means it fifty times will "ON" and "OFF” in one second.
Which figure you saw above, this is one "AC current"
cycle, exactly like this 50 cycles will crossed in 1 second. You watching that
voltage start from "0" point go to upward, how much it will go to
upward this is depend on "AC" voltage, again it coming to downward
and touch to "0" point.
Afresh start from "0" point and goes to downward, once
more how much it will go to down it is depends on voltage, and again it going
to upward and will touch to "0" point and complete a cycle, this
process will continue in the same way.
The any electrical appliances for running need voltage and
current. When any equipment will run on “AC” current then another waveform
create with voltage. Which waveform will be of the current, but this both
waveforms run together in one also wire.
Just like that:-
One waveform is of the
voltage and other waveform of current so which space or angle between these two
waveforms this is power factor. That is, if there is a difference between
voltage and current, it will be called power factor.
Point no.1 (Sometimes the current is ahead of the voltage and
sometimes the voltage is ahead of the current, and sometimes they are
together.)
Now we discuss about that why this different in power
factor. Which was discussed in above point no.1 like voltage and current etc.
We have three types of Power factors.
- Unity power factor
- Lagging power factor
- Leading power factor
Define: - 1 Unity Power Factor
The unity means is “1” and this is best power factor because in this voltage and current moving together. Means voltage and current waveform touch together to "zero" point both of them will travel jointly.
Define: - 2 Lagging Power Factor
The lagging power factor between “0.1” to “0.9” and this is not best power factor, because in lagging power factor get power loss. Means it’s not good in which voltage and current not move together. In voltage and current's waveform create some angle or space. In the lagging power factor voltage start first but current will start after some mille seconds, in its waveform voltage first touch to the "0" point, then current will touch to the "0" point.
Define: - 3 Leading Power Factor
The leading power
factor is also between “0.1” and “0.9” and it is not the best power factor
because the leading power factor lacks power, which means it is not good. it
will not run voltage and current together some angle or gap is created in the
waveform between voltage and current. The current in the leading power factor
starts first but the voltage starts after a few milliseconds, in its waveform
the current first touches the "0" point, then the voltage touches the
"0" point.
Why Power factor divided in three types?
The power factor is divided into three types according to the electrical load.
1- Unity
power factor
2- Lagging
power factor
3- Leading power factor
1- Resistive load
Which load having
high resistance and energy spend by heating is called Resistive load, this
type's load always has unity power factor. Means its power factor is “1” so
this type’s load or appliances is best it not has any power losses.
The Resistive load such as Cloth press iron, Water Geyser, Electrical Cattle, Room Heater, Soldering Iron, Hair Dryer, etc.
2- Inductive load
The equipment in which having the winding or inductor, and the energy expended by the magnet is called inductive load. this type of load always has legging power factor, i.e. its power factor will be less than “1” like “0.9” or “0.1”, so these types of devices give power loss.
The Inductive loads such as Motor, Fan, Refrigerator, Grinder Machine, Compressor, Etc.
3- Capacitive load
The capacitive load
is none, this type of load that we own is made from inductive load with the
help of capacitor, we connect the APFC panel to our load, because the capacitor
can convert legging P.F to unity power factor.
You have read above
that capacitive load creates the leading power factor, i.e. the current moves
forward, etc. And the inductive load create lagging P.F, so in this P.F current
running behind from voltage.
Now understand
better by example:-
Suppose: -
A motor that is running normally will have its power factor in lagging, for example the current is running 30 degrees behind the voltage, if we connect a capacitor whose current moves 30 degrees forward, so this means that the previous time was 30 degrees behind the current from voltage and after the connected capacitor current 30 degree ahead, so now voltage and current will touch the "0" point together, for this we get the unity power factor because if current and voltage touch the "0" point together then it is called unity power factor.
Power factor formula
cos(θ) = W / VA
Example: - A water
heater consume 600 watt on 220v
W / V = A
W = Watt
V= Volt
A= Current or Ampere
Solve by
Mathematically
First step:
600w / 220v = 2.72A
Second step
Now put power
factor formula
W / VA = cos(θ) or
P.F
600 / (220 * 2.72)
220 * 2.72 = 598.4
600 / 598.4 = 1.002
Means this Unity Power Factor because it is resistance load.
END



0 Comments
Post a Comment